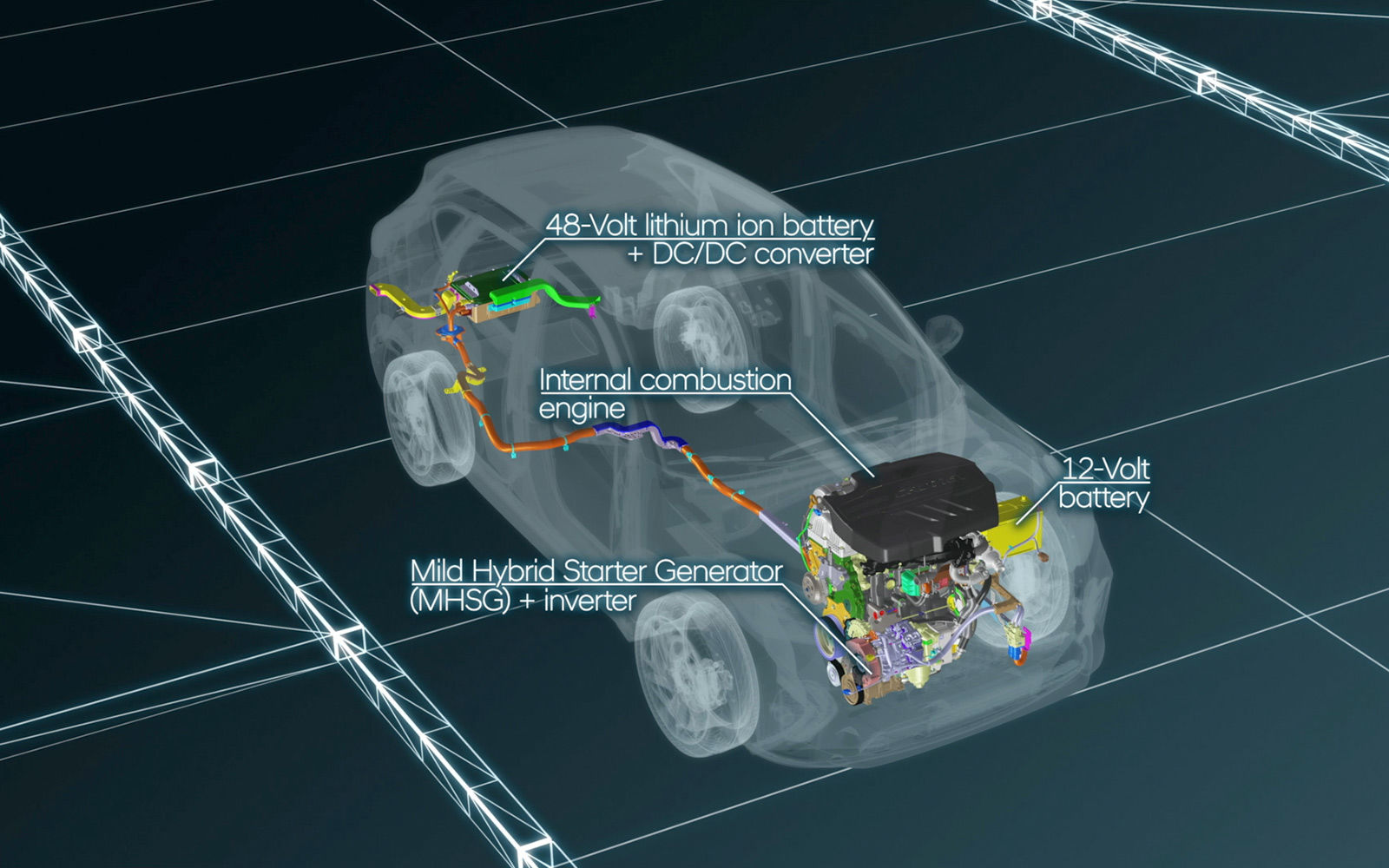
In addition to the 2.0-litre CRDi 48-Volt diesel powertrain introduced in the New Tucson in 2018, Hyundai Motor has now combined its efficient and responsive 48-Volt mild hybrid technology with the 100 kW/136-PS 1.6-litre CRDi diesel engine.
[ads id=”9″]
The technology comprises a 48-Volt battery, a Mild Hybrid Starter Generator (MHSG) and LDC converter (Low Voltage DC/DC). In addition to the 48V electrical system, the vehicle is equipped with the conventional 12V electrical system, which is connected via the DC/DC converter to the 48V system. Thus, parts of the energy stored in the 48V battery system can also be used to stabilise the 12V on-board power supply.P
The 0.44 kWh 48V lithium-ion battery, which supplies the mild hybrid system with electric energy, is located beneath the rear luggage compartment, while the MHSG is mounted to the combustion engine. A belt connects the MHSG to the crankshaft of the internal combustion engine. The MHSG generates kinetic energy from recuperation of up to 12 kW and 55Nm of torque at the MHSG shaft.
Hyundai’s Mild Hybrid technology as used with the New Tucson significantly improves the powertrain’s fuel economy and CO2 emissions by up to 11 per cent* depending on the vehicle specification. (*NEDC 2.0) As an additional benefit, the system supports the internal combustion engine, compensating with power during the different stages of driving, and helps lead to a faster and smoother engine start. Thus dependence on the internal combustion engine is reduced.
Comfortable start and take-off
The mild hybrid system has particular advantages in city traffic, with the MHSG supporting the combustion engine when re-starting after traffic stops. This action supports a faster and smoother engine start with supplemental torque, drawing on energy from the 48V battery. As a result of the earlier and faster delivery of torque, the engine start can be anticipated by 0.2 seconds. The conventional 12V starter is only used for the initial starting operation if the engine oil is still cold and a higher starting torque is required.
The MHSG assists the combustion engine during take-off by compensating with torque and power.
[ads id=”8″]
Efficient and boosted acceleration
Under acceleration, the MHSG supports the combustion engine with compensatory 4 to 12 kW of power, depending on the battery system’s state of charge and the degree of accelerator input from the driver. Once the required speed is reached, the MHSG shifts to neutral mode, delivering no power. As a result CO2 emissions, as well as fuel consumption, can be reduced by up to 11 per cent.* (*NEDC 2.0)
Constant driving
At a constant speed, the MHSG either is at idle or acts as a generator charging the 48V battery, depending on the battery state of charge.
[ads id=”8″]
Recuperation
In active braking or overrun phases, the rotating crankshaft powers the MHSG, which then acts as a generator with a maximum recuperation output of 10 to 12 kW. The generator converts the kinetic braking energy into electricity, and feeds it back into the 48V battery. In these phases, the combustion engine remains switched on and clutch kept closed to be able to transfer the power from the wheels over the transmission and the engine to the MHSG.
Extended start-stop
When coasting at low speeds, the start-stop function already activates at 30 km/h. Under deceleration between 30 and 0 km/h, and with the clutch disengaged, the engine is switched off completely.
Additional models to be equipped with mild hybrid powertrain
With the additional mild hybrid powertrain for its best-selling model in Europe, Hyundai is further expanding its electrification strategy to make clean technologies accessible for even more customers. Thanks to the mild hybrid system, customers benefit from a good trade-off between purchase cost and reductions in fuel consumption and CO2 emissions.
The highly efficient system has been developed at Hyundai’s European Technical Center in Germany and Hyundai’s R&D Center in Namyang, Korea. It will be available in combination with more engines in the future, as part of the company’s highly diverse mix of electrified solutions.
[ads id=”8″]