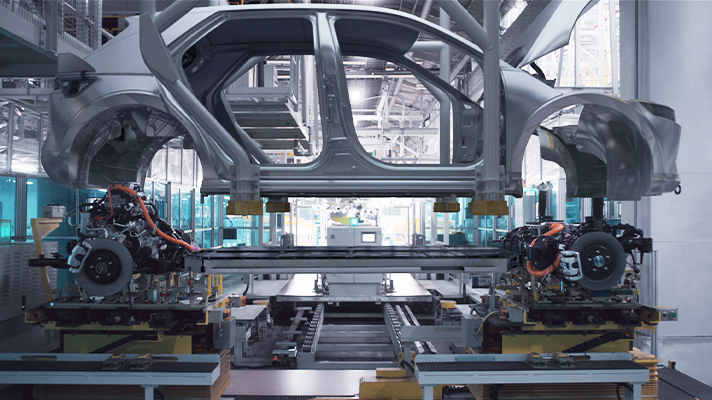
The IONIQ 5 is the first electric vehicle to apply E-GMP (Electric-Global Modular Platform), a dedicated platform, and is the result of Hyundai’s latest technology for eco-friendly vehicles. The South Korean carmaker released an interesting video where we can see how the new IONIQ 5 manufacturing process.
The state-of-the-art production process of the IONIQ 5, where next-generation technology and eco-friendly materials are precisely intertwined, is the birthplace of smart mobility and a blueprint for a sustainable future. In addition, through the video, you can vividly see the innovative manufacturing process of parts that are only applied to dedicated electric vehicles, such as ICCU (Integrated Charging Control Units), PE system (Power Electric System), and battery pack, which are key elements of the IONIQ 5.
We looked at the advanced automation process of IONIQ 5, which is the birthplace of smart mobility and presents a blueprint for the smart factory that Hyundai’s aims for.
The core element ‘ICCU’ that performs V2L, the representative function of IONIQ 5

The video of the production process of the IONIQ 5 starts with the assembly of the ICCU. ICCU is a Hyundai’s newly developed integrated charging system to charge both the high-voltage battery and auxiliary battery installed in electric vehicles.
In ICCU, all manufacturing processes are performed automatically, from moving, assembling, and welding individual parts to moving the finished product. Due to the nature of power supply devices that require a clean working environment and precision, the production line is installed in a clean room.
ICCU is absolutely necessary to use V2L (Vehicle to Load), a representative function of IONIQ 5. Existing electric vehicles were only capable of one-way charging, which delivers external power to the inside of the vehicle.
The IONIQ 5 can supply 3.5kW of power, which is higher than the 3kW contracted power for general housing, through the V2L function, and can operate a 17-pyeong air conditioner and a 55-inch TV simultaneously for about 24 hours depending on battery capacity. You can also use the IONIQ 5 as a large power bank to operate electronics or charge other electric vehicles in outdoor activities or camping sites.
Electric vehicle drive system ‘PE system’ in which the motor, reducer, and inverter are integrated
The next scene in the ICCU manufacturing process is the PE system, which is an electric vehicle drive that replaces the powertrain of an internal combustion engine vehicle. The PE system of E-GMP, which is the basis of the IONIQ 5, is characterized by integrating the motor required for driving, the reducer that converts power to the torque and speed required for the vehicle, and the inverter that converts power and controls the torque of the motor. to be. Due to this, the PE system of E-GMP is significantly reduced in size and weight compared to the existing system.

The drive motor applied to the PE system of the IONIQ 5 uses a hairpin winding method, which is a high-level construction method. Hairpin winding technology literally means a structure using a rectangular cross-section coil that resembles the shape of a hairpin (hairpin). After the robotic process of assembling the hairpin windings and the coil-wound stator is completed, the workers’ elaborate connection work is added to complete the complex internal structure. After that, the PE system in which the motor, reducer, and inverter are integrated is assigned a unique number and ready to be mounted on the IONIQ 5.
A ‘battery pack’ where cells and modules come together to form one
In the process of assembling the battery pack, which is the power source for electric vehicles and the heart of the IONIQ 5, the harmonious movements of robots are reminiscent of semiconductor production lines. The battery pack of the IONIQ 5 consists of 12 cells, the basic unit of a battery, to form a standardized module, and the modules combine to form a pack.
A battery cell is a basic unit of a lithium-ion battery that can be used by charging and discharging electrical energy. The positive electrode, negative electrode, separator, and electrolyte are placed in a pouch-shaped case in advance and delivered to the factory. The pouch-type battery cell used for E-GMP can satisfy the desired energy capacity with a small number of battery cells, and has excellent competitiveness in manufacturing cost and manufacturing process.

The battery module refers to a battery module assembly (BMA) that is bundled in a certain number and put in a frame to protect cells from external shock, heat, vibration, and the like. Hyundai Motor Group developed E-GMP and standardized battery cells and modules. Thanks to this, when the battery is damaged, it can be replaced in a module unit rather than the entire battery, which not only reduces repair costs, but also improves manufacturing and quality competitiveness.
A battery pack is the final form of a battery system mounted on an electric vehicle, and is composed of a certain number of modules. The battery pack of the IONIQ 5 is divided into a basic type and a constant type according to specifications, and the number of modules mounted in the pack changes accordingly. Based on E-GMP, the Ioniq 5 has a 10% increase in energy density compared to conventional electric vehicles that use the same size battery due to a standardized battery system, making it possible to configure a more efficient and lightweight battery system.

Battery pack assembly starts with the process of attaching a pad made of a porous material to the cell. When an operator loads a PU (polyurethane) pad on the work plate, the automation equipment vacuums the pad and peels off the double-sided film. After that, the pad with the peeled film is reattached to the cell and fully adhered by applying high pressure.
In this process, the key is that the automation equipment controls the characteristics of the PU pad, which is prone to problems due to the influence of static electricity. The cell with PU pad is moved to the next process after checking whether it is attached to the correct position and whether the film is normally peeled through the vision system, an automated visual inspection using a camera.
In the subsequent process, a 6-axis articulated robot stacks 12 cells on a conveyor one by one to make one module. Since the location of individual cells has a decisive effect on battery quality, we move the cells to the correct location within the range of 0.2mm deviation. Considering the characteristics of cells that are easily damaged, all facility operations are carried out while maintaining proper pressurization.
The battery module installed in the IONIQ 5 was newly developed for E-GMP, Hyundai’s dedicated electric vehicle platform. It is for this reason that the size of the battery module in the video is very compact.
After that, several modules are gathered to form a pack. The battery pack assembly process starts by covering the upper case with the lower case equipped with BMA, bus bar (a rod-shaped conductor that enables electrical connection), electrical cables, and gaskets to keep the pack tight.

The upper and lower cases of the battery are fixed with a total of 70 bolts and nuts. At this time, after checking the exact position information of the bolt and nut using the vision system, the information is transmitted to the 6-axis articulated robot equipped with a nut runner (power tool that tightens the nut). When the 6-axis articulated robot automatically tightens the bolts and nuts based on the set standard, the battery pack assembly process is completed.
‘Unmanned transport device’ that can meet the future smart factory in advance
The completed battery pack is loaded onto Hyundai’s Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) that moves along a path on the stored map and transported to a predetermined location. The unmanned transport system is a system that autonomously avoids surrounding obstacles and finds the optimal route to the destination through wireless communication and collision avoidance sensors, and increases productivity by autonomously driving.
The advantage of the unmanned transport system is that the working environment and safety are improved because the operator does not have to manually drag heavy parts. In addition, parts can be moved at the correct time and place through real-time control, and the size of the factory is optimized by minimizing the movement of unmanned transport devices, while quality control of parts is easy. Hyundai’s smart factory is characterized by applying innovative automation methods such as artificial intelligence (AI) and robot technology.
Body assembly to complete the appearance of the IONIQ 5

The battery pack, which is loaded onto the unmanned transport device and moved to a designated place, meets the ICCU, PE system, front and rear suspension, and drivetrain to complete the E-GMP platform. In this way, while the E-GMP platform is sequentially completed, the body of the Ioniq 5 is manufactured on the other side.
The work process continues from the body line, which completes the appearance by assembling the panels and skeletons that make up the body, to the painting line for coloring. After the industrial robots assemble the body with modest movements and finish painting with flexible and delicate movements, the IONIQ 5 finally has its appearance.
After combining the E-GMP platform and the body into one, it is ready to move to the design line to fill in the details. In order to greatly increase the battery protection performance of the IONIQ 5 during the assembly process, an 8-point mount that is fastened with long bolts from the bottom of the battery to the inside of the body floor is added.
When detailed elements such as headlamps/tail lamps, windshield/windows, wheels/tires, instrument panel/infotainment screen, and various electronic equipment/sensors are added to the IONIQ 5, the familiar IONIQ 5 is completed.
‘Intensive battlefield inspection’ to secure the reliability of the Ioniq 5’s battlefield quality

Hyundai’s IONIQ 5 with various battlefield systems goes through a battlefield intensive inspection process to check whether various functions are working properly. The computer inputs the set data, and according to the data, various sensors such as cameras and radars work properly and quickly and accurately.
The IONIQ 5 is equipped with a Surround View Monitor (SVM), a Head Up Display (HUD), a Front Corner Radar, and a Digital Side Mirror through the corresponding inspection system. Check and correct functions, etc. The electronic inspection system that checks the normal operation of advanced electronic equipment and various systems is characterized by reducing variations in quality and increasing reliability.
After intensive electric field inspection, the IONIQ 5 production process is finally completed after the last process, the design line, is added with the skill and touch of skilled workers and goes through the final quality check process.
Hyundai’s IONIQ 5 was born based on the smart factory ecosystem
As seen above, IONIQ 5 is born based on a smart factory ecosystem that pursues innovation in manufacturing systems. Hyundai’s smart factory is aiming for uses information and communication technology (ICT) to collect and analyze all system data within the factory, including product quality control, production facilities, and logistics, as well as external information, into big data. It is a system that runs a factory.
Smart factory operation using artificial intelligence and big data aims to create the best products for consumers. The goal is to eliminate unnecessary processes and increase the accuracy and efficiency of product production based on accurate data.

In the meantime, Hyundai Motor Company has put a lot of effort into building a smart factory ecosystem so that it can produce a variety of cars quickly and efficiently in one space by introducing an innovative and advanced automated production method to respond to individual customer needs agilely.
Prior to building a smart factory, various production technologies were also developed. In 2017, it introduced a smart tag system consisting of a location tracking sensor, a high-capacity memory, and a wireless communication chip. This system is a technology that helps the assembly robot figure out what kind of car it is and assemble it. Hyundai’s full-length intensive inspection system, unveiled in 2018, is a system that has improved the efficiency by changing the ADAS quality inspection that was conducted over several processes to a single process method using six cooperative robots.
Hyundai’s artificial intelligence technology, which is considered a key technology for building a smart factory, is also being applied. It is raising the level of automotive painting quality through deep learning scanning recognition technology for painting inspection paper that combines artificial intelligence technology with the automobile painting inspection process.
IONIQ 5, which was created through a smart factory ecosystem based on an electric vehicle-only platform. The next-generation smart mobility that will provide a new mobility experience, IONIQ 5, is expected to change the mobility industry environment in the future.
Source: HMG