Hyundai Motor is expanding its offer of energy solutions by developing Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) technology. V2X is a technological innovation that further integrates renewable energy and battery electric vehicles (BEV) into society.
One of these technologies is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G). This technology enables energy that is already stored in the battery packs of BEVs to be provided to an electricity network, also known as a ‘grid’. On top of stabilising the grid, the energy stored in BEVs feeds the grid to assist in managing energy demand during peak times and emergencies. Hyundai is currently running two V2X pilot projects in the Netherlands and Germany featuring fleets of modified IONIQ 5 models that are equipped with customised V2G-capable software.
The energy landscape will drastically change due to this integration of BEVs into the grid. Not only will BEV owners have the opportunity to contribute actively towards the stabilisation of their local grid, but V2G will also be a strong contributor to a stabilised renewable energy provision. The grid directly distributes renewable energy from solar or wind power to users. With the application of V2G, renewable energy can be stored in BEVs and fed back to the grid when it cannot be generated, for example at night or when there is no wind, or at peak times.
As V2G technologies benefit not only BEV owners but also entire societies sharing an energy system, this initiative falls in line with Hyundai’s “Progress for Humanity” vision.
The benefits of V2G
As a convenient and cost-efficient way to locally store and share energy, V2G offers numerous benefits for BEV owners, the grid, and the environment.
When V2G technology balances the grid, everyone benefits. During high-peak times when large amounts of energy are drawn from the grid, BEVs can return energy to the local infrastructure and help even out the demand. Owners can then recharge their BEVs at a lower cost during off-peak hours.
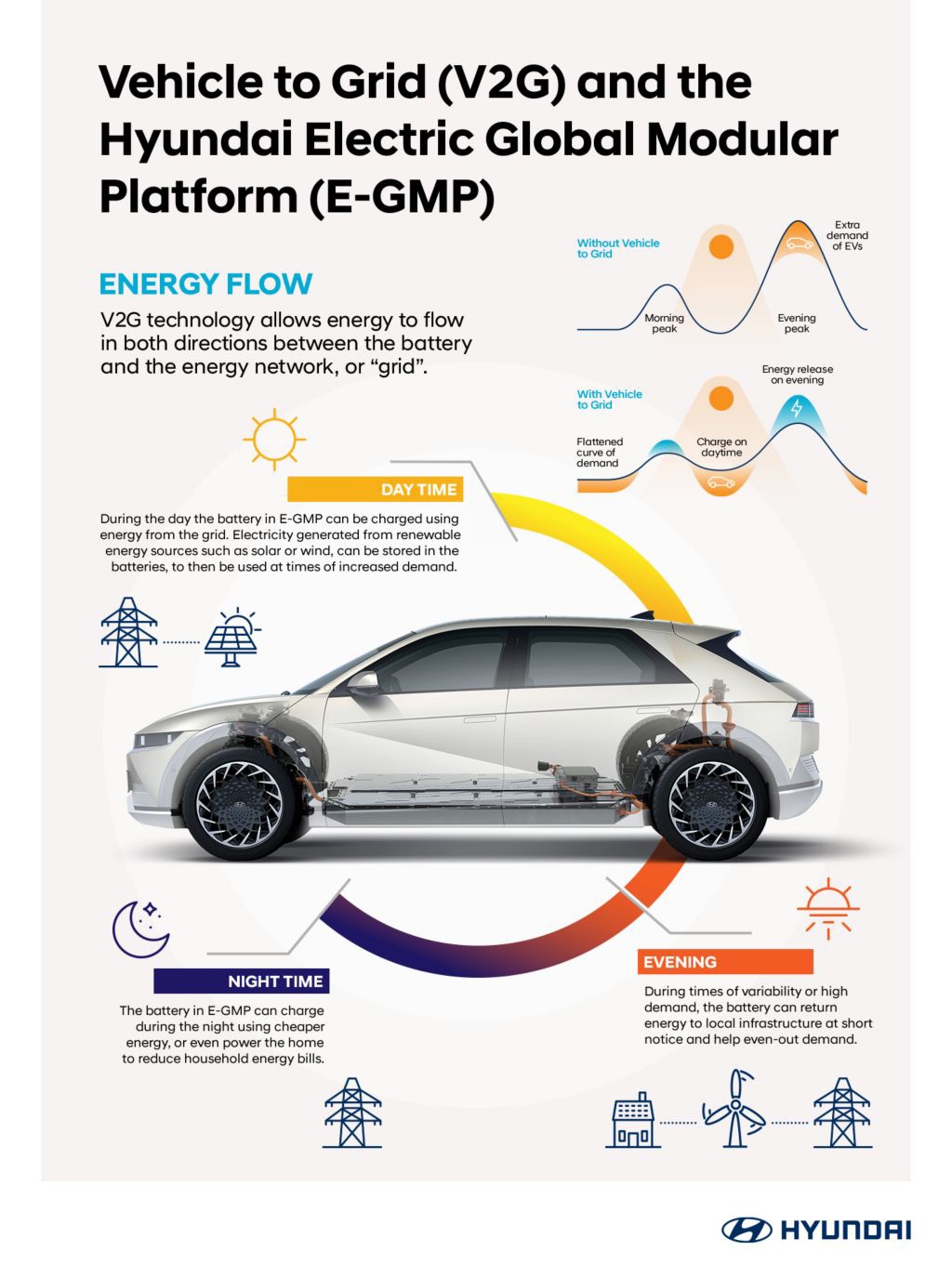
According to business models that are currently under review, users can provide energy from their BEVs into the grid. Because grid services are used more efficiently, V2G results in savings for operating electricity systems, which are then passed on to the user. Additionally, the entire system can reap economic benefits from these reduced power system costs because V2G offsets capital and operational costs.
Hyundai’s future with V2G
Electric Global Modular Platform (E-GMP), Hyundai Motor Group’s first BEV dedicated platform, already features Vehicle-to-Load (V2L) technology, which allows bidirectional charging. It is planned for the bidirectional onboard charger that enables V2L to also support V2G in the future.
V2L and V2G have similar technical principles regarding reverse power transmission; however, the technologies utilise different software. Since V2G needs to provide the grid with energy, a communication protocol between the BEV and the grid must first be defined.
Developmental projects for V2G are currently in progress at Hyundai, and the company plans to announce an upcoming BEV model with V2G technology.






